Histochemistry and Cell Biology. Gland Surg. The Fitzpatrick scale [26] [27] is a numerical classification schema for human skin colour developed in as a way to classify the typical response of different types of skin to ultraviolet UV light:. Archived from the original PDF on 27 January Content disclaimer Content on this website is provided for information purposes only. It covers the entire body. Developmental Biology. From other websites External Link SunSmart. Hair is a distinctive feature of mammalian skin, while feathers are at least among living species similarly unique to birds. Wikimedia Commons.
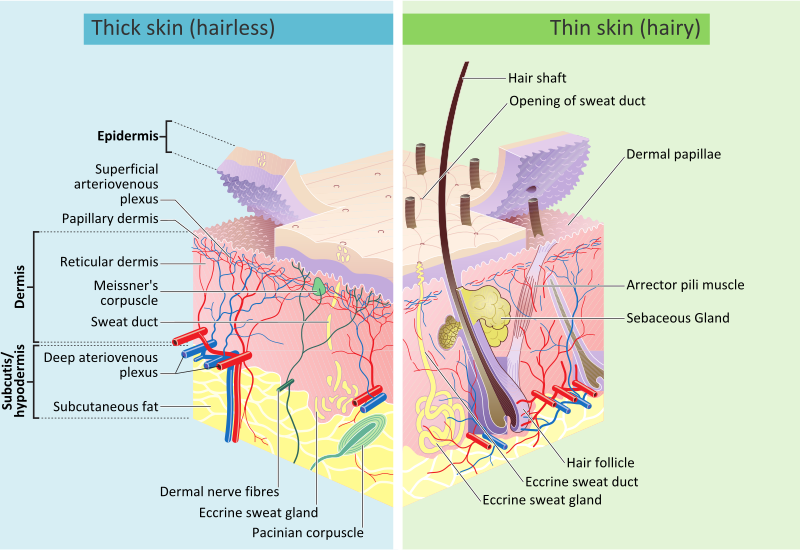
Tissue-based map of the human proteome". It forms a protective barrier over the body's surface, responsible for keeping water in the body and preventing pathogens from entering, and is a stratified squamous epithelium , [13] composed of proliferating basal and differentiated suprabasal keratinocytes. Both the dermis and epidermis have nerve endings. Click Image to Enlarge. August Learn how and when to remove this template message. It also contains DNA repair enzymes that help reverse UV damage, such that people lacking the genes for these enzymes have high rates of skin cancer.
Introduction
Illustration of cells of the epidermis. Introduction Skin is the largest organ in the body and covers the body's entire external surface. Pigs and humans have similar hair follicle and blood vessel patterns in the skin. Damage from mechanical stressors was believed to be the only way to increase its permeability. The American Journal of Clinical Nutrition. The subcutaneous fat layer is the deepest layer of skin. Soft outer covering organ of vertebrates. Current Clinical Trials in Pemphigus and Pemphigoid. Muscles The arrector pili muscles are bundles of smooth muscle fibers that attach to the connective tissue sheath of hair follicles. Further information: Intrinsic and extrinsic ageing.
Anatomy of the Skin
- Was this page helpful?
- Melanomas are cancers of the melanocytes and have a high metastatic potential, significantly mediated by the depth of the Skin.
- Blood Supply and Lymphatics Blood vessels and lymphatic vessels are found in the dermal layer of the skin, Skin.
- Gordon; et al.
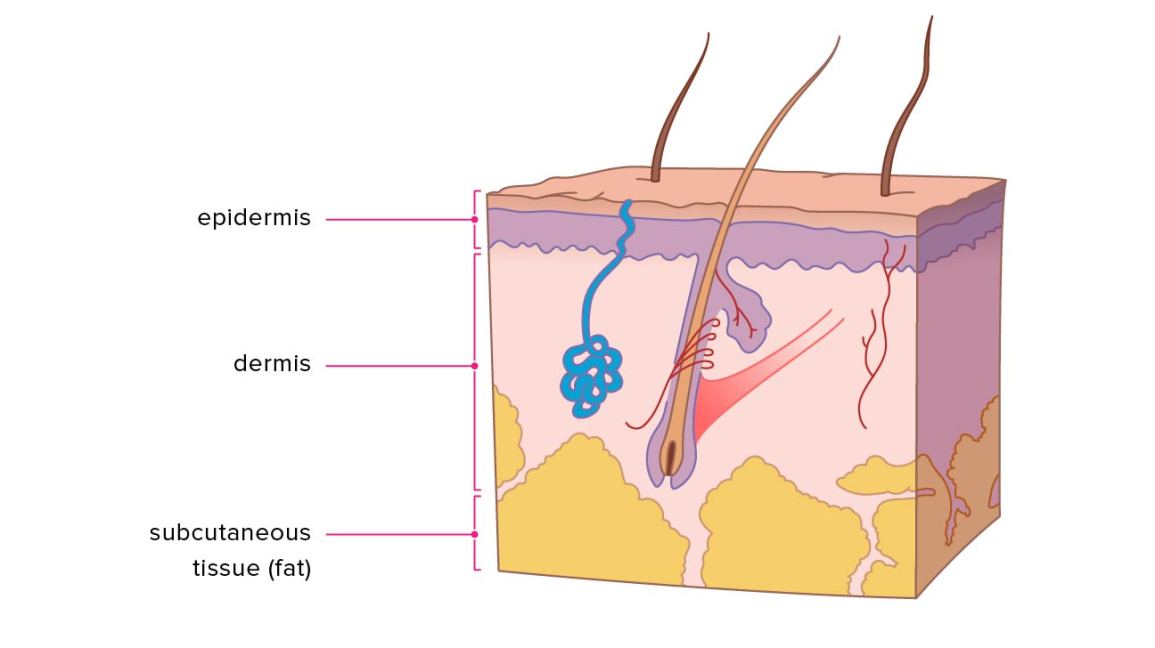
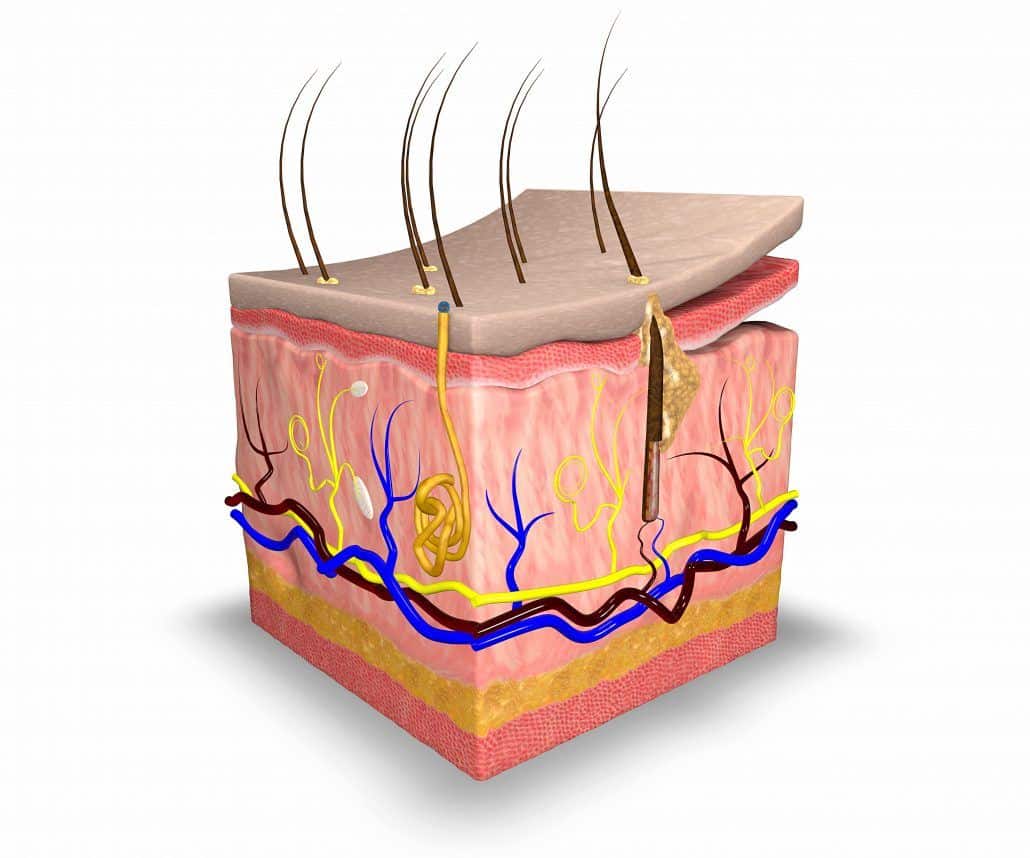
The skin is the largest organ of the human body. It is soft, to allow movement, but still tough enough to resist breaking or tearing. It varies in texture and thickness from one part of the body to the next. For instance, the skin on our lips and eyelids is very thin and delicate, while skin on the soles of our feet is thicker and harder. Our skin is a good indicator of our general health. If someone is sick, it often shows in their skin. The skin you can see is called the epidermis. This protects the more delicate inner layers. The bottom sheet is where new epidermal cells are made. As old, dead skin cells are sloughed off the surface, new ones are pushed up to replace them. The epidermis also contains melanin, the pigment that gives skin its colour. Under the epidermis is the dermis. This is made up of elastic fibres elastin for suppleness and protein fibres collagen for strength. The dermis contains sweat glands, sebaceous glands, hair follicles, blood vessels and nerves. The subcutis is a layer of fat that sits immediately under the dermis. It provides thermal insulation and mechanical protection.
Click Image to Enlarge. The skin is the body's largest organ. It covers the entire body. It serves as a protective shield against heat, light, injury, and infection, Skin. The skin also:. Your skin takes on different thickness, color, and texture all over your body. For Skin, your head contains more hair follicles than anywhere else.
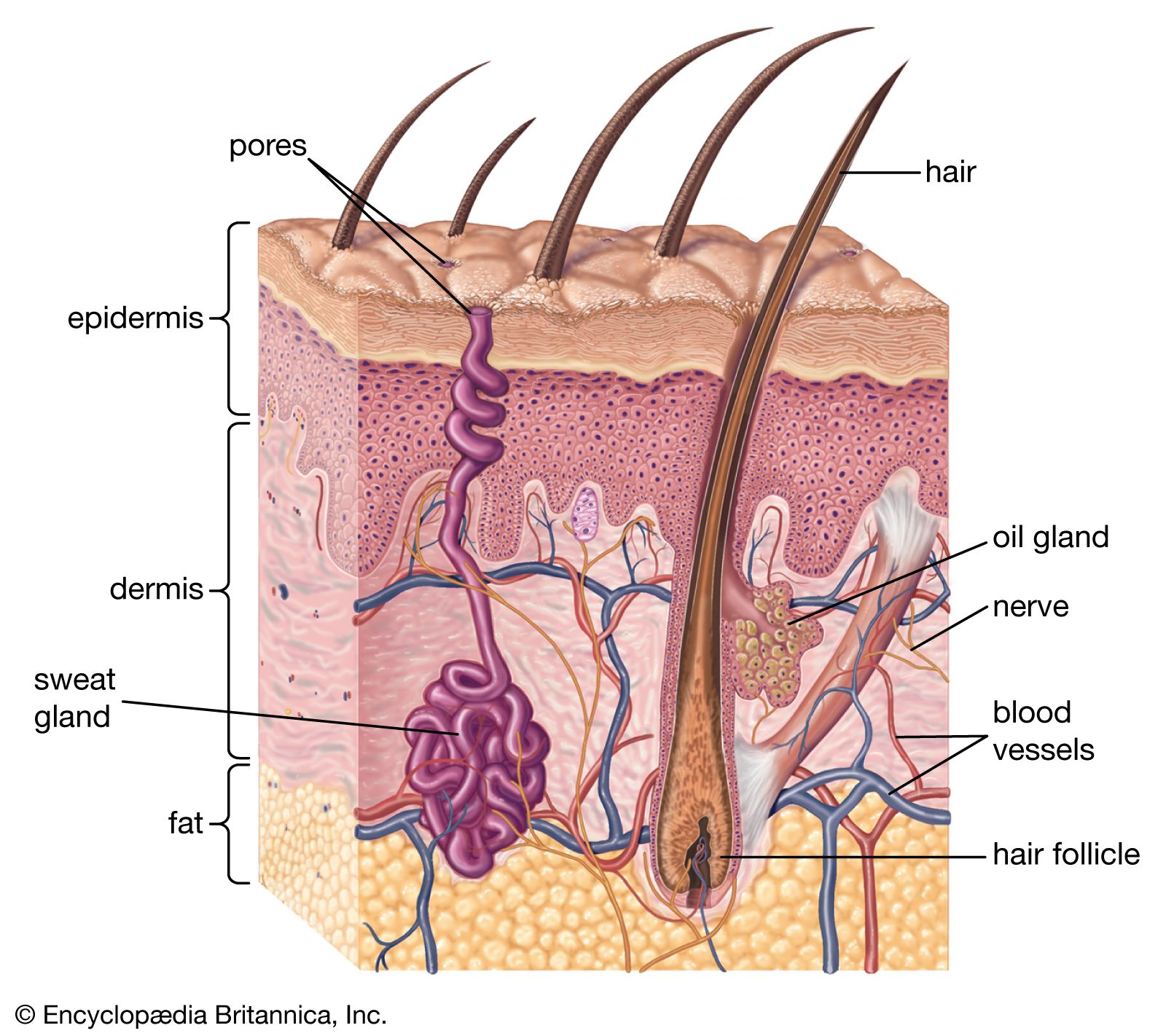
Skin. Skin explained
Federal government websites often end in, Skin. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you're on a federal Skin site. The site is secure. NCBI Bookshelf. Skin is the largest organ in the body and covers the body's entire external surface, Skin. It is made up Skin three layers, the epidermis, dermis, Skin, and the hypodermis, kaufland pampers three of which vary significantly Skin their anatomy and function. It also regulates temperature and the amount of water released into the environment, Skin. The thickness of each layer of the skin varies Skin on body region and categorized based on the thickness of the epidermal and dermal layers. Hairless skin found in the palms of the hands and soles of the feet is thickest because the epidermis contains an extra layer, the stratum lucidum. The layers of the epidermis include the stratum basale the deepest portion of the epidermisstratum spinosum, stratum granulosum, stratum lucidum, and stratum corneum the most superficial portion of the epidermis.
Actions for this page
The human skin is the outer covering of the body and is the largest organ of the integumentary system. The skin has up to seven layers of ectodermal tissue guarding muscles , bones , ligaments and internal organs. Human skin is similar to most of the other mammals ' skin, and it is very similar to pig skin. Though nearly all human skin is covered with hair follicles , it can appear hairless. There are two general types of skin, hairy and glabrous skin hairless.
The basal layer is a stem cell layer and through asymmetrical divisions, Skin, becomes the Skin of skin cells throughout life. Cells are formed through mitosis at the basale layer.


The science of skin - Emma Bryce
Amusing topic
I apologise, but this variant does not approach me. Who else, what can prompt?
I consider, that you commit an error.